Updated October 2024 - Wireless WAN is now a viable alternative to wired infrastructure and is being used for primary connectivity by a range of Australian enterprises.
Climate disruption, a distributed workforce, and the expansion of the network edge, are all reasons why Australian IT teams should be considering adding Wireless to their WAN.
Wireless brings increased flexibility, security and reliability to networks.
The impact of bushfires, floods and the pandemic on Australian communications infrastructure highlights the benefits of wireless as part of the enterprise network.
Severe weather events, floods and bushfires have all reeked havoc with Australia's communications infrastructure in the past two years, with wired connections being particularly vulnerable.
At the same time the post-pandemic workforce remains widely distributed, and the use of cloud-based applications for work and play is now the norm.
Each of these factors alone supports a compelling business case for including wireless as a component of the enterprise network.
What are the market drivers for Wireless WAN?
Fixed locations no longer define enterprise networks – businesses need to connect people, vehicles, pop-up locations, kiosks, cloud services and an ever-expanding universe of IoT devices.
Wireless WAN is becoming essential to expand the reach of enterprise networks and deliver fast, secure and flexible connectivity where ever work is happening.
1. Link diversity for business continuity
Adding diverse types of network connectivity to create a more reliable WAN is a primary reason for introducing wireless.
Wireless broadband provides a diverse and protected connection that avoids terrestrial challenges like backhoes digging up lines, or falling trees. Further, with SD-WAN and QoS capabilities, organisations can precisely control network traffic while ensuring high availability.
2. Secure, Agile and Scalable Networks
For many organisations, the importance of business agility and enhanced security has come to the fore because of the pandemic. The business requirements for these capabilities will not disappear in a post-pandemic world. In many ways, the challenges of recent times have forced many organisations to realise what is possible with the help of Wireless WAN.
Cloud-managed wireless edge solutions utilising LTE and 5G are simple to deploy and easy to relocate. Routers and adapters can be effortlessly moved to a new room or site without the pain and expense of pulling new outside cable.
Whether a branch location is being turned up or a short-term event needs networking, making use of WWAN can be the difference between success and no network at all, especially in difficult-to-wire locations.
3. Supporting a distributed workforce
Working from home introduces new security risks as users access data and applications that were once only accessed behind a security perimeter. WFH has also led to an increase in real-time communications application traffic (voice, video, online meetings) on networks. As a result, IT staff need to provide a secure network infrastructure to support work-from-home and work-from-anywhere on a more permanent basis, and for many, do it with the same staff and resources they have today.
Using a dedicated wireless WAN connection can extend secure connectivity to the employee's home with the same IT capabilities and end-user experience as the office network. Cloud management can provide visibility, remote diagnostics, out of band management and end user support.
4. Expansion of the Network Edge
For several years, edge computing has been trundling along as a niche deployment model. But the use cases and workloads that benefit from the edge computing model are starting to move into the mainstream.
The early goal of edge computing was to reduce the bandwidth costs associated with moving raw data from where it was created to either an enterprise data centre or the cloud. More recently, the rise of real-time applications that require minimal latency, such as autonomous vehicles and multi-camera video analytics, are driving the concept forward.
The ongoing global deployment of wireless WAN, especially 5G, ties into edge computing because 5G enables faster processing for these cutting-edge, low-latency use cases and applications.
Is Wireless WAN viable in Australia?
Cellular wireless networks are an appealing alternative to traditional wired network infrastructure because they provide fibre-fast and cellular-simple connections anywhere you can get a cell signal.
As cloud applications, mobility, and IoT devices continue to proliferate, the Wireless WAN enables a flexible and unified approach to connecting people, places, and things anywhere.
The arrival of 5G has made a wireless WAN a viable alternative to fixed connections. , while improved antenna to tower technologies and spectral efficiencies also increase the number of devices, connections and throughput that each 5G tower can support.
Already 5G-embedded routers are delivering high performance, matching and exceeding the speeds of NBN. At the Westpac Helicopter Base at Botany Bay, Sydney, MobileCorp has installed a Cradlepoint 5G Adapter that is regularly achieving speeds of 800+Mbps down and 70 Mbps up. This performance will become commonplace as the 5G signal density grows across Australia.
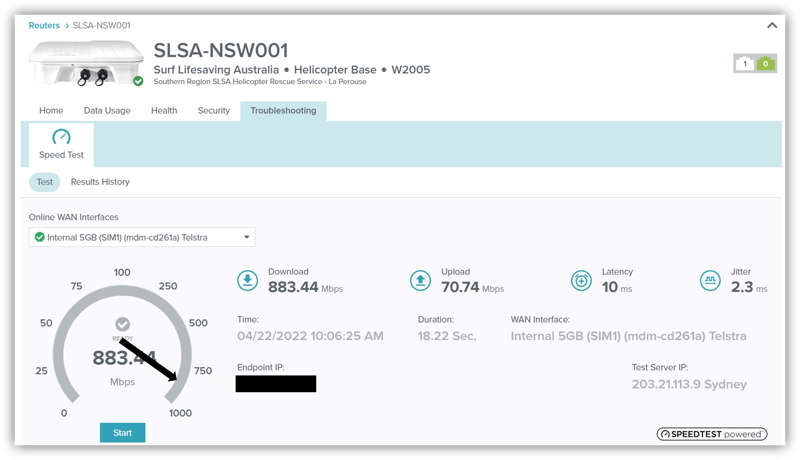 Credit: Cradlepoint 5G speed test at La Perouse Helicopter Base April 2022
Credit: Cradlepoint 5G speed test at La Perouse Helicopter Base April 2022
Is Wireless WAN new?
Wireless technologies are already a common feature of daily life in 2022, from smart home links to satellite-based ISP connections. For most of us Wi-Fi has become our main network access method, backed up by cellular broadband connections.
The historical shift from wired Ethernet LANs to Wi-Fi is a great example of the future trajectory for wireless WAN. Offering improved reliability, security, reach and bandwidth, Wi-Fi overtook wired LAN with its competitive flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
LTE and 5G are having similar impacts on wired-only WANs. So, while wireless WAN is not a new concept, 5G is the emerging technology that is enabling the improved performance of wireless WAN.
What is Wireless WAN used for?
Cellular wireless has always been ideal for business continuity and for connecting critical assets in places wires can’t go, like vehicles, field forces, and remote kiosks. It has also been useful for temporary or new locations where wires would take weeks or months to deploy.
However the use cases have expanded as today’s 5G cellular networks become more pervasive.
At the same time, carriers like Telstra are making cellular a more attractive option with evolving pricing options, shared data, and Telstra has launched the world-first 5G Enhanced Enterprise Wireless solution which provides a guaranteed 99.9% 5G network uptime.
These realities are ushering in the Wireless WAN era and giving rise to wireless becoming a more attractive connectivity option for branches, stores, and other fixed sites — the last exclusive domain of wired networks.
Five Key Wireless WAN Use Cases
These five use cases are driving forward the adoption of enterprise wireless WAN across Australia. MobileCorp has collaborated with a range of companies to deploy networks that address these needs.

#1. Protecting the network with automated failover
Non-stop availability is critical for the cloud era. Cloud application utilise the WAN like a LAN. If the WAN goes down, the applications are no longer usable. The same is true for mission-critical applications like point-of-sale. Tens of thousands of businesses around the world leverage 4G LTE and now 5G to provide a non-stop infrastructure that is immune the loss of a wired connections.
Additionally, wireless failover connections can also be used for Out-of-Band Management (OOBM). If a remote site needs centralised troubleshooting, OOBM can provide the remote access needed without depending on a wired connection.
#2. Augmenting network bandwidth to manage traffic
SD-WAN technology allows for the aggregation of multiple connections to generate greater bandwidth. Here, adding a wireless connection alongside wired is a powerful way to increase bandwidth while increasing availability. With advanced LTE reaching speeds up to 350 Mbps, and 5G at over 1 Gbps, wireless connectivity is now fibre-fast and cellular-simple.

#3. Making wireless the primary link
One thing that cellular does better than wired is reach. It can go places where wires don’t or where wired options are limited and not business-class.
Additionally, using cellular wireless as a primary WAN connection makes sense for pop-up or temporary sites given the fact that wired options can take up to three months to get installed.
Another key use case for primary wireless connections is for remote work. Rather than companies having to deal with hundreds of different wired ISPs to serve their employees, that can often accomplish the same with one national wireless carriers. Moreover, using cellular provides a second link into the home for redundancy.
Finally the branch office which has traditionally been the last bastion of the wired network, is also a prime target for wireless.
#4. Expanding IoT capabilities at the edge
While many people think of IoT in terms of occasional data that has little impact on the existing network, when it comes to many IoT use cases - such as video surveillance, telehealth, and automated manufacturing - large amounts of data is generated that needs to be transmitted over the network.
Cellular wireless is unique in that is can support everything from very low to very high bandwidth IoT applications within the same wireless WAN, secured by the same tools, and managed by the same platform
Enhanced antenna and transmission techniques massively increase the number of devices and conversations that each wireless links can handle, making wireless support for IoT networks and other high-density applications a reality.

#5. Adding Vehicles to the enterprise WAN
As businesses become more mobile, equipping their fleets with wireless networking, both inside and out, is a way to keep field workforces and things always connected to the applications that make them productive. Next-generation WANs are moving beyond the branch, and beyond wires, to connect people, places and things, anywhere.
Some industries are centred around a connected vehicle - police, fire, couriers, taxis, marine - with connectivity critical to deliver a service.
About MobileCorp
MobileCorp is an enterprise ICT solutions company with a mission to deliver our customers a communications technology edge. We provide Managed Mobility Services, Enterprise Mobility Management, Complex Data and IP Networks, and Unified Communication solutions. We have a proven track record providing managed services for Australian enterprise and business, and we are a Telstra Platinum Partner.
5G Michelle Lewis 13 Jul 2022
Related Posts
Popular Tags
- Mobile Devices (82)
- Mobility (81)
- Telstra (66)
- 5G (65)
- MobileCorp Managed Services (55)
- Mobile Network (38)
- Networks (34)
- Cradlepoint (32)
- Apple (29)
- MobileCorp (29)
- iPhone (25)
- Remote Working (23)
- Network (17)
- Covid-19 (16)
- Mobile Security (15)
- Wireless WAN (15)
- Cyber Security (14)
- UEM (14)
- MDM (11)
- Mobile Expense Management (10)
- Mobile Device Management (9)
- TEMs (9)
- Mobile Device Lifecycle (8)
- Cloud (7)
- Unified Comms (7)
- Unified Communications (7)
- Wandera (7)
- Android (6)
- Sustainability (6)
- Data Networks (5)
- Network Security (5)
- Samsung (5)
- Security (5)
- Digital Experience (4)
- IOT (4)
- Microsoft Intune (4)
- Blog (3)
- IT Services (3)
- Microsoft (3)
- Data (2)
- Government (2)
- Microsoft 365 & Teams (2)
- Retail (2)
- nbn (2)
- webinar (2)
- 4G (1)
- DAS (1)
- EMM (1)
- Emerging Technologies (1)
- Hosted Telephony (1)
- Managed Desktops (1)
- SD-WAN (1)
- Starlink (1)
- Telstra Services (1)
- WWAN (1)
- video (1)










